Nearly everyone has experienced the discomfort of low back pain at some point. It can be a seriously disabling illness for many people.
If you’re here, you probably have low back pain or know someone who does. It’s a surprisingly common problem, affecting millions of people each year. The question is, what is it? Furthermore, what treatment option is available?
This article will examine low back pain, its causes, and how to treat it. We’ll also look at some lifestyle factors contributing to low back pain and other related conditions. We will also discuss how physical therapists can help to improve this condition. So if you’re looking for information on low back pain, you’ve come to the right place.
What is low back pain?
Low back pain is an uncomfortable pain located near the lower spine. To understand the causes of low back pain, you must know about the muscles spanning the lumbar region.
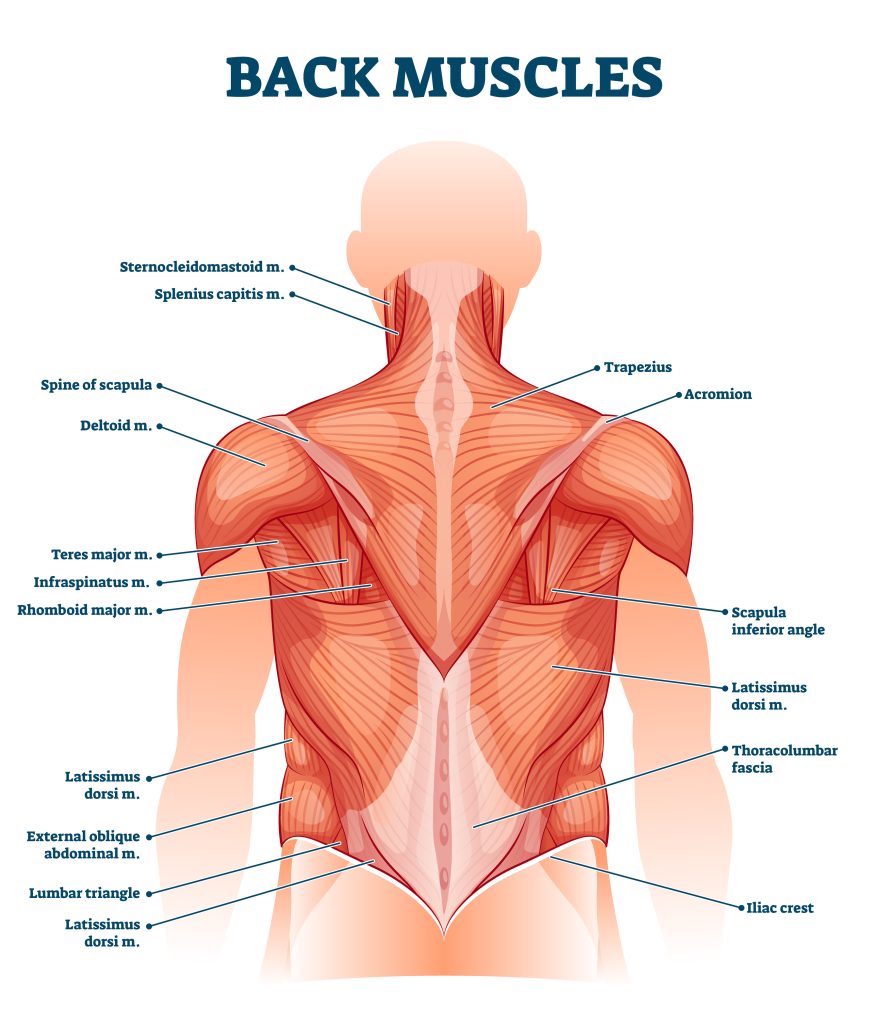
The space between the lumbar vertebrae is known as the intervertebral discs. They include several discs that act as pistons maintaining the weight pressure on the vertebrae.
After leading a rough lifestyle, pressure on the discs and then osteoarthritis in the joints cause the discs to become injured and crack. The damaged discs and associated nerves are called herniated discs.
Low back pain can cause a great deal of discomfort and interfere with daily activities. It is essential to seek treatment if you are experiencing any symptoms of low back pain.
What causes low back pain?
Many things cause this condition. The wide range of possible triggers might be challenging to identify the precise source of this condition. Some of the most common causes include:
- Injury or trauma to the back
- Sitting for long periods
- Heavy lifting
- Osteoarthritis
- Spinal stenosis
- Herniated disk
- Low back tension can create pain if it does not limit spinal motion and movements.
- Other illnesses like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis can lead to low back pain.
What are the symptoms of low back pain?
Even though there isn’t a clear definition of “back pain,” here are some of the most common symptoms of this condition:
- Pain in the back that worsens when you bend
- Pain that worsens when you lift or change positions
- Back pain that radiates to other regions
- Pain that radiates from the back and feels like someone is stabbing you with a knife
- Pain accompanied by muscle weakness
- Discomfort brought on by a strain or compression on the tissues surrounding a nerve root
- Pain that worsens with activity.
It’s important to remember that the injury, pain, and damage may be permanent for reasons other than their anatomical nature. In other words, the pain may originate from another fractured vertebra. An injury to a muscle, tendon, ligament, or nerve contributes to the intensity of the pain through tension or traction.
However, keep in mind that back pain is not a disease or an abnormality in the body. It’s just the vertebrae’s generally up and down movement, supported by the muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints.
Classifications of low back pain
Some of the causes of low back pain are related to injuries, but most cases of back pain can be classified as follows:
- Nerve Root Compression: Under some circumstances, the space in your back can become so narrow that it causes problems with the nerves that go to your spine, resulting in illustrations of back pain. Click here to read more.
- Injury: An injury triggers the inflammatory response to a bone, muscle, or ligament. Even minor injuries are possible to these parts, so it is vital to follow preventative care so that damage does not worsen.
- Spinal Malignancies: Growing or developing tumors, whether neurological or not, can impede the health of nerves leading to the spinal cord. Here’s an article for further reading.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Posture, genetics, and heredity can make it easier for your spine to become weak and make your ligaments or bone start to deteriorate. In this case, it can result in direct trauma through the cartilage, bones, or ligaments. Click here to learn more.
With prompt treatment, you can loosen mobility in the solution. Many medical types of research have shown us that some cases of back pain have a genetic origin.
How to diagnose?
The first step in diagnosing low back pain is to determine its cause. Low back pain has many different reasons, and the diagnosis will vary depending on the grounds. Muscle strain, herniated disks, spinal stenosis, and arthritis are some of the most prevalent causes of low back discomfort.
Once the cause is determined, a doctor or physical therapist can develop a treatment plan. Medication, physical therapy, or surgery are only some choices, depending on the nature of the problem.
What are the treatment options?
Short-term home remedies for low back pain:
To ease back pain in the short term, you can use over-the-counter painkillers, ice packs, and heat therapy.
- Ice packs can help with inflammation in the area.
- Heat therapy is great for chronic back pain.
- A massage is great for relieving muscle tension. If you are in pain, do not massage the area — you can worsen the pain.
- Medications: Medications can also help treat low back pain. Multiple medications are available, depending on the cause of the pain.
Some of the treatment options for low back pain include:
While over-the-counter medications can often treat low back pain with over-the-counter medications and lifestyle changes, there are times when more aggressive treatment is necessary.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy is an excellent option for those who want to treat their low back pain before resorting to more aggressive treatments. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility.
- Surgery: If other treatments have failed, surgery may be necessary. Various surgeries can be performed to treat low back pain, depending on the underlying cause.
Low back pain exercises:
Recommended are the following low back pain exercises to prevent and treat lower back discomfort. Do them daily, up to twice a day.
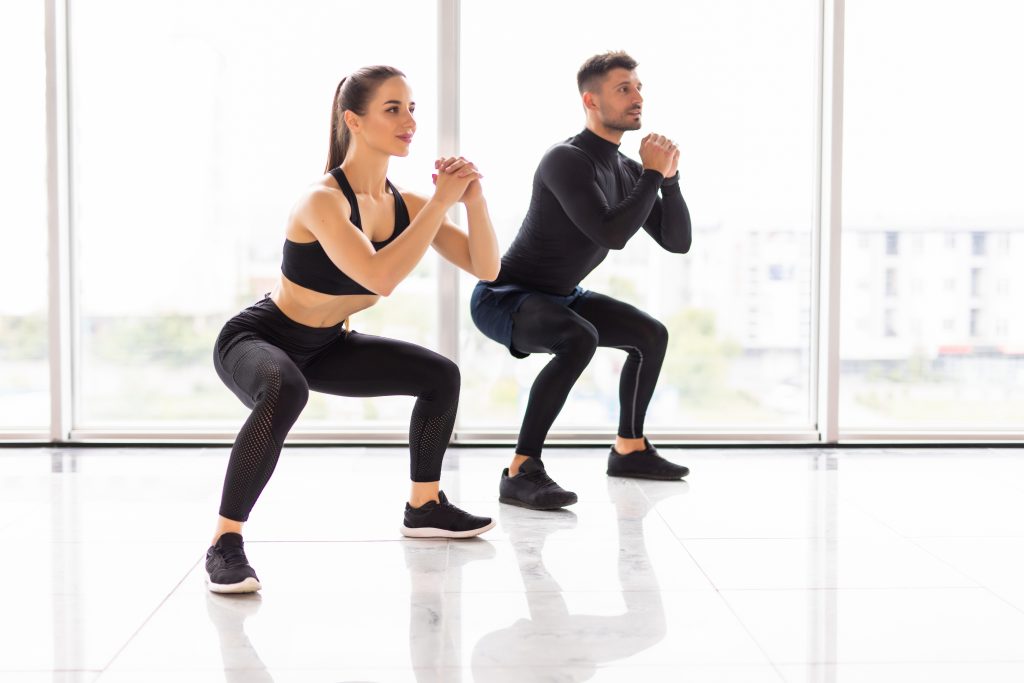
- Squatting has many benefits, one of which is strengthening the core. This exercise helps in reducing back pain.
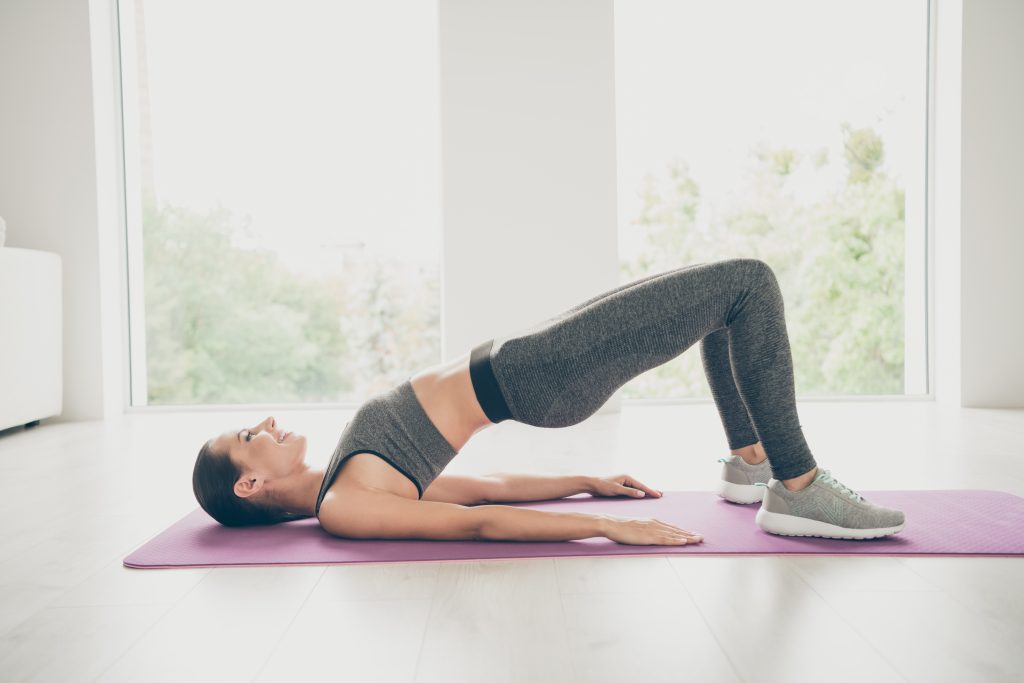
- Bridge: This is an extension of the squat exercise. You can do it while lying down, and it’s an excellent exercise for your lower back, hips, and core.
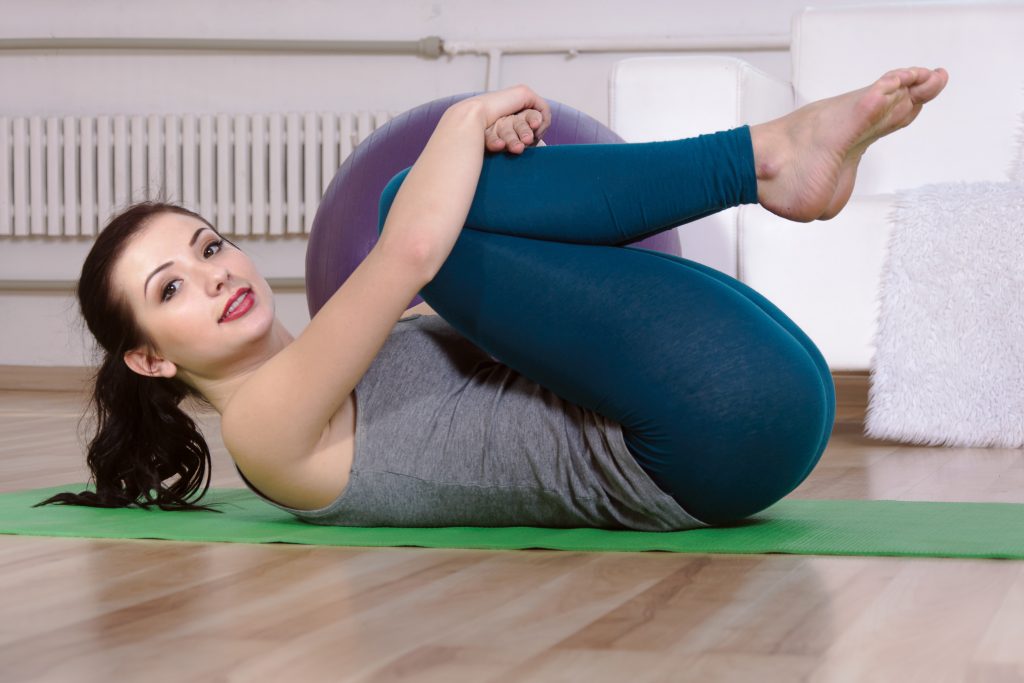
- Knee-to-chest stretch: The knee-to-chest stretch stretches the muscles of the hip and low back (lumbar spine). It should also alleviate pressure on the spinal nerves by providing more space for the nerves as they exit the spine.
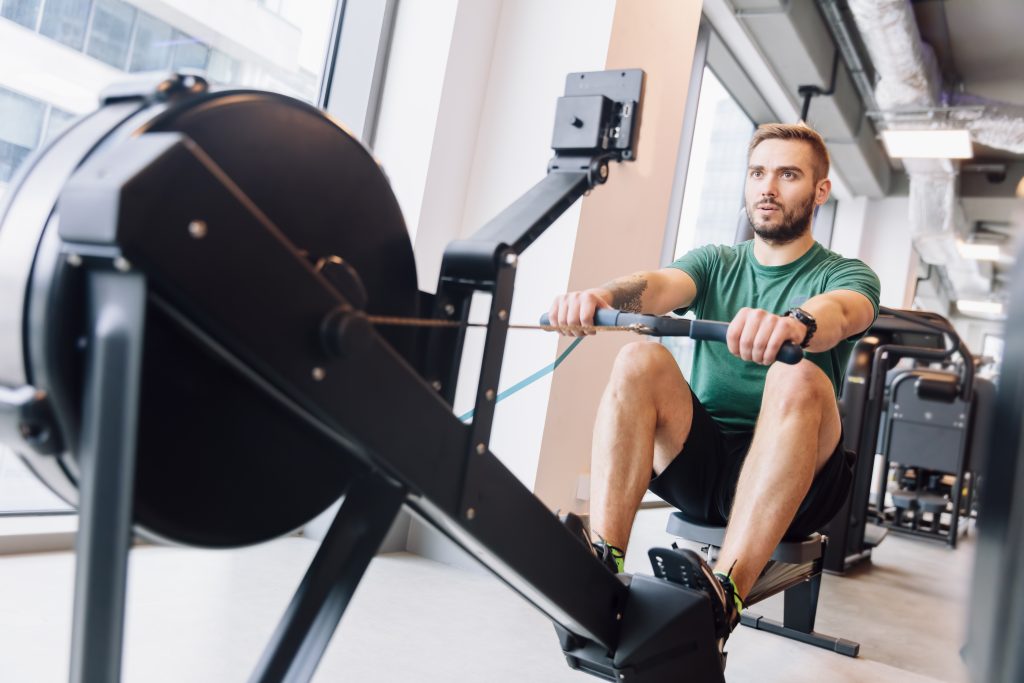
- Row: This is an excellent exercise to strengthen your upper back and the core. You can do it seated or standing.
- Plank: This is a wonderful exercise for strengthening the abdominal muscles. It also helps in improving your posture.
- Yoga: This is an excellent option for those new to exercise. It helps reduce stress, improve your posture, and strengthen your core.
Prevention
- Practice good posture: This is the best way to prevent back pain. Incorporate it into your daily routine, and you will see results. You can use posture bracelets as a reminder to keep your posture in check.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise is therapeutic and helps strengthen your core. It also improves your aerobic fitness, improving your strength and stamina.
- Sleep well: While getting enough sleep is essential, it’s just as important to sleep correctly. The ideal sleeping position for your back is on your back.
- Maintain a healthy diet: What you eat directly affects your overall health. A healthy diet is essential for good nutrition and a balanced intake of vitamins and minerals.
- Wear the right shoes: Wearing the right shoes is crucial to your overall health. They affect your posture and back, so choose wisely.
- Manage stress: Stress is inevitable, and we all must deal with it. Meditation, yoga, and unplugging from social media are just a few techniques to handle stress.
Takeaway
Many people find that back pain persists for more extended periods than expected. In cases of minor back pain, simply lying in bed can cause pain to recur. Fortunately, medication, physical therapy, and proper exercise can help relieve pain and keep it from recurring.
A progressive strengthening program and stretching can help prevent low back pain from occurring and will also help to relieve pain if it does happen.
We hope that this information was helpful. Despite this, we must point out that low back pain is prevalent. Healthcare professionals can treat it in a variety of methods. There is no one-size-fits-all answer, so coordinating with a healthcare professional is essential to determine your optimal treatment strategy.









